Israel
Improving land-based mariculture to meet growing demand and comply with regulations
Challenge
As the Earth’s population expands, access to fresh, healthy, sustainable food is an ever greater challenge
Fish farming systems are the fastest growing food production sector in the world, providing 47% of global fish supplies.
Traditionally, the water used in fish farming tanks is treated to convert harmful waste from fish into less toxic elements, called nitrates. Yet, these nitrates and other pollutants that remain in the water are typically released into lakes and oceans, where they can cause excessive algae and plant growth, overwhelming water-based ecosystems and harming wildlife. This is why new global environmental regulations require these nitrates to be removed from fish farming systems.

Project Ô has developed the SALTECH module as a simple to operate and cost-effective nitrate removal process for land-based mariculture
It remove nitrates, other pollutants and excess salts from the water, which enables it to be sustainably reused in fish tanks or to water plants.
These technologies also allow for valuable nutrients to be recovered from the wastewater, which can then be used as fish food or processed further to be used as biofuel or green fertilisers. This process also maintains a stable water temperature, which is very important to improve the management of disease control. This allows the fish to grow bigger and healthier.
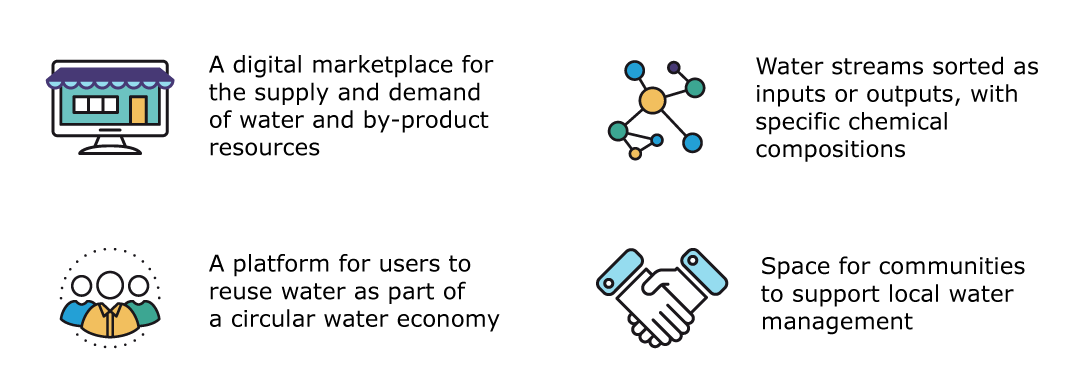
Project Ô has developed a Circular Economy Platform (CEP) to support local water reuse
The aim is to provide a marketplace for different users involved in water treatment activities
This web application will encourage a circular water economy by providing the best matches between water demand, water flows and treatment technologies.

Background
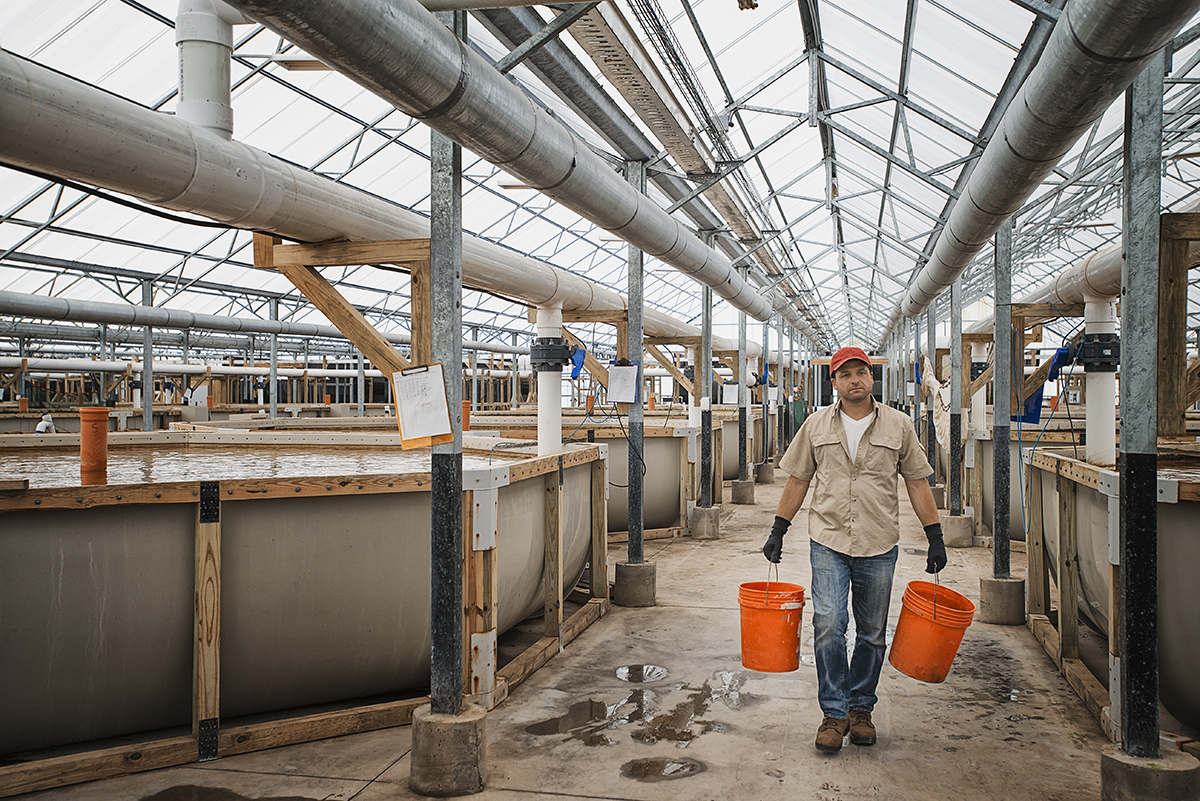
The National Center for Mariculture is based in Eilat, the southernmost city in Israel
NCM promote the development of mariculture as a unique branch of aquaculture
Land-based mariculture relies on the recirculation of water to remove waste. The water is filtered and treated to remove substances like ammonia which is converted to less toxic nitrates but current technology cannot remove nitrates and other pollutants, which can then build up in the tank. Environmental regulations now require nitrates to be removed.
Historically, water use has been linear, with water extracted
from one area, used and then discharged elsewhere

Project Ô has developed SALTECH technology to become part of the mariculture treatment process to remove nitrates and other pollutants. This enables an almost 100% closed loop of reused water, with the only water requiring replacement being that lost through natural evaporation. As well as meeting new environmental legislation, the system will be more efficient and cost-effective. Using CEP will provide a meeting point for various users involved in water treatment activities to circulate resources.
Developing environmentally-friendly systems for rearing fish is a key priority for NCM. While taking a circular economy approach has created the potential for additional commercial opportunities, such as providing nutrient-rich water to fertilise nearby crops.
Circular Water Economy
By using Project Ô water treatment technologies, water can be reused sustainably in fish farming systems. This means meeting the growing need for healthy food while using less water, protecting the environment from the negative impacts of harmful wastewater, and making full use of available nutrients, thereby reducing the demands on finite resources.
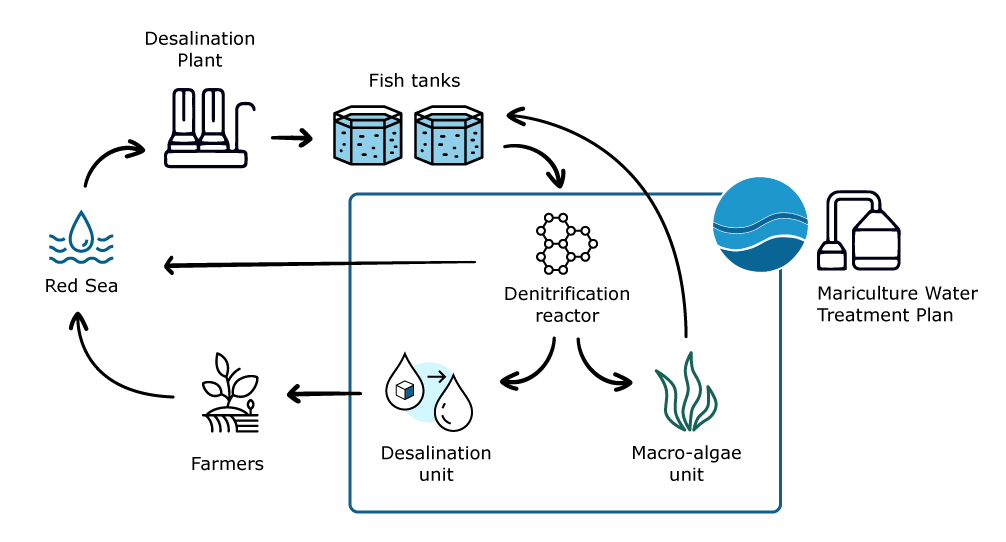
Project Ô technologies have helped close the loop on water use in mariculture at Eilat in Israel
And this leads to other benefits too...

Solution
SALTECH technology removes nitrates and other pollutants and helps recover nutrients from land-based mariculture systems
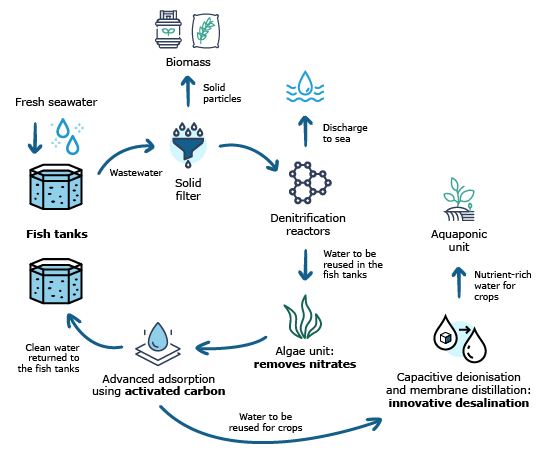
It has been designed to meet environmental regulations for good mariculture practise
Through the removal of nitrates and other pollutants, less “raw material”, in the form of additional seawater, is required. By reusing more water, a small percentage of “new” seawater is introduced to the system. The benefits of SALTECH technology include:

Using SALTECH technology provides opportunity for commercial expansion
Part of SALTECH technology includes an algae-based biofilter system, which needs mass production of algae for its operation.
This creates an opportunity for commercial expansion. Algae can be used in food, as feed, for cosmetics and health, in green chemistry or as a biofuel.
Using the desalination feature of SALTECH technology could also produce a commercial product. This nutrient-rich water can be used to support the production of salt-tolerant crops in arid areas like Eilat.
CEP is designed to allow businesses to participate in a circular water economy
CEP will enable local trade of water and by-products between different water users involved in water treatment activities